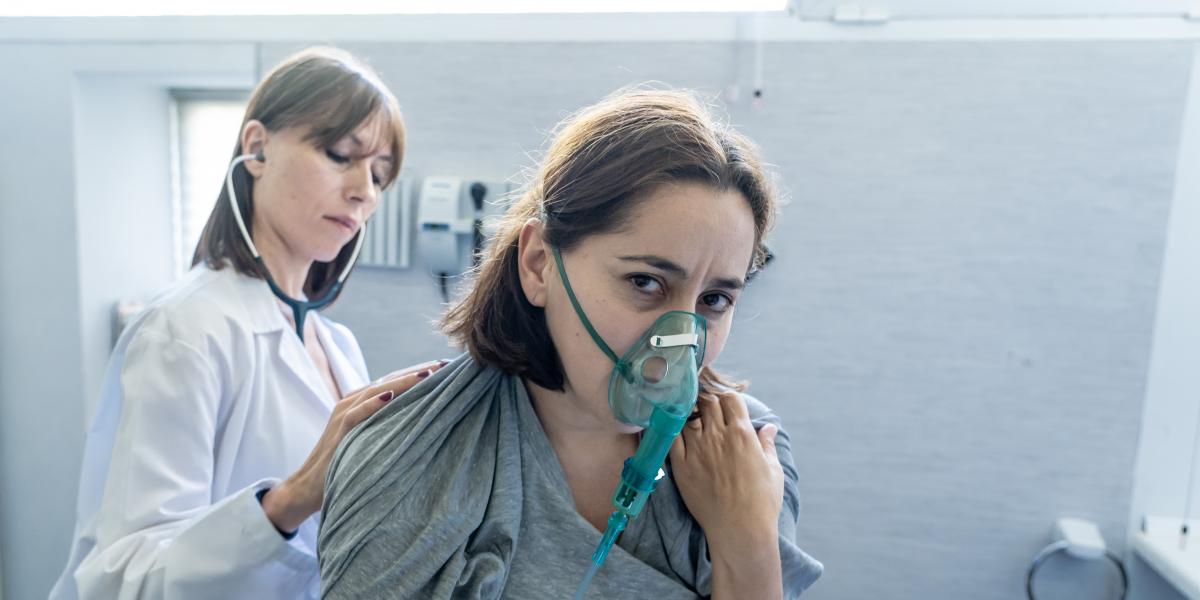
An infection in one or both of the lungs is known as pneumonia. Fungi, viruses, and bacteria can cause pneumonia. When a person has pneumonia, the alveoli or air sacs in the lung are filled with pus or fluid. This causes moderate to severe trouble breathing and can cause other symptoms as well. When a person has pneumonia, they are contagious. It can be spread through airborne droplets from a sneeze or cough. People can acquire pneumonia if they touch surfaces that have the pneumonia virus or bacteria on them. The only pneumonia that is not contagious is fungal pneumonia. This is caught from the environment and is not spread from person to person. To prevent pneumonia, people should wash their hands frequently and avoid anyone that is sick. This is especially true for older people and those with weakened immune systems.
Types and Causes of Pneumonia
There are several causes of pneumonia, and these include:
- Bacterial pneumonia - This is a commonly seen form of pneumonia, and the common cause is Streptococcus pneumoniae. It can also be caused by legionella pneumophila, mycoplasma pneumoniae, and haemophilus influenzae.
- Viral pneumonia - Viral pneumonia can be caused by respiratory viruses, the flu, and rhinoviruses. Viral pneumonia is mild and will clean up within a couple of weeks.
- Fungal pneumonia - This type of pneumonia is caused by fungi in bird droppings or in the soil. This is commonly seen in people with weakened immune systems.
Types of pneumonia include:
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia - This is where people who are in the hospital using a ventilator get pneumonia.
- Community-acquired pneumonia - This is when a person contracts pneumonia outside of a hospital setting.
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia - This is typically a bacterial pneumonia that is acquired during hospital stays. This type of bacteria may be more difficult to treat due to being resistant to antibiotics.
- Aspiration pneumonia - When a person has swallowing issues, they may get aspiration pneumonia. This is caused by food, drink, or saliva going down the wrong way and getting into the lungs.
Signs and Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can vary from being mild to life-threatening. Symptoms may vary from person to person, depending on the type of pneumonia and the cause. Symptoms include:
- Fever
- Sweating
- Chills
- Coughing
- Increased phlegm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- No appetite
These symptoms may also vary by age. For example, an older person may experience mild symptoms, but have lower than normal body temperatures and confusion. A child under five years old may have wheezing, while an infant may vomit and have trouble eating or drinking. If a person suspects that they have pneumonia or a family member does, a trip to the doctor should happen immediately. With early treatment, the symptoms of pneumonia may be minimized. Left untreated, pneumonia can become extremely life-threatening.
Getting Treatment
Treatment options for pneumonia will vary depending on the severity of the pneumonia and the type. A doctor may prescribe medications like antibiotics to treat a pneumonia infection. If the pneumonia is viral, a person may be given an antiviral to help. Typically, viral pneumonia will clear on its own without the antiviral. If a person has fungal pneumonia, they will be given medication to counter the fungus.
The doctor may recommend pneumonia sufferers take over the counter medication for fever and pain. Cough medicine may be recommended to help ease the cough. The doctor will also recommend plenty of fluids and rest. For severe cases of pneumonia, hospitalization may be required. At the hospital, medications may be given through an IV. A person may also get oxygen therapy and respiratory therapy to help ease and treat the symptoms.
It is important to note that whatever treatment options are given that they are followed well. If they are not followed, the pneumonia may return, or the symptoms may increase in severity.