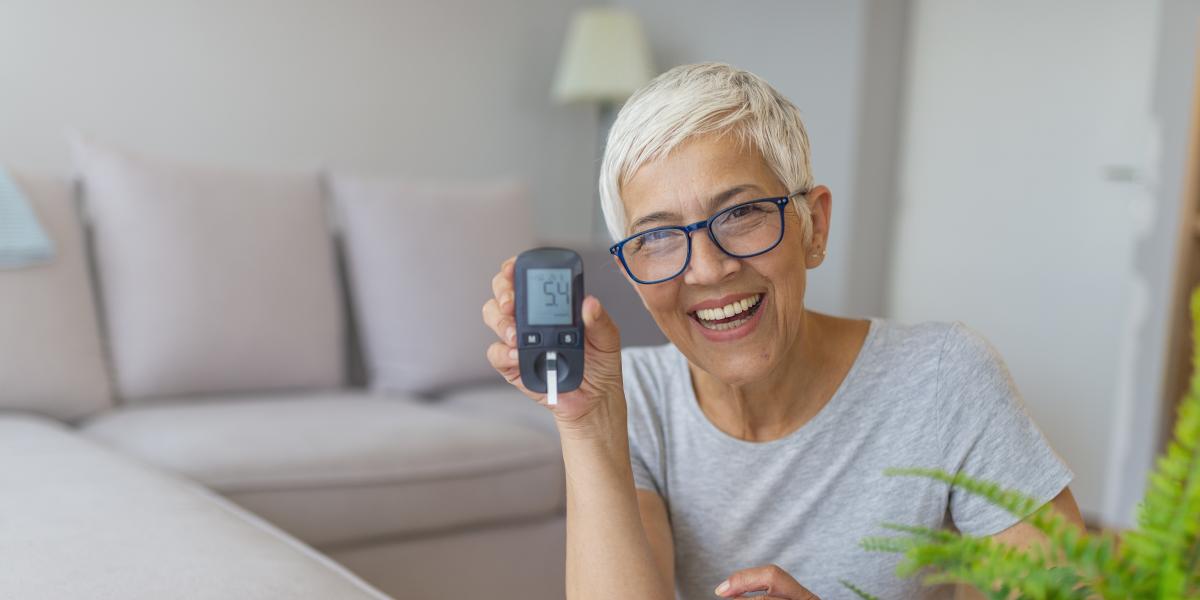
Diabetes is a health condition that involves a peptide hormone protein. This protein allows your cells to use the sugar, or glucose, you ingest through your diet. Cells require glucose as fuel. It is the body’s main source of energy. When someone has diabetes, it means that their body either doesn’t produce an adequate amount of the protein or cannot use it properly. This causes the glucose to end up trapped in the bloodstream. This can lead to serious health problems.
Types of Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Both are chronic. Type 1 diabetes usually appears in childhood, while type 2 diabetes most often appears during adulthood, though it can also appear during childhood. In addition, prediabetes is a potentially reversible condition that can lead to type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes is another form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy but may disappear after a woman gives birth.
How Common is Diabetes?
In the United States, diabetes affects 9.3% of the population, or approximately 29.1 million people. Of those people, 1.25 million have type 1 diabetes. An estimated 8.1 million people are living with undiagnosed diabetes. Among seniors, the prevalence of diabetes is even higher, at 25.9% or 11.8 million people, including both diagnosed and undiagnosed individuals. Each year, approximately 1.4 million Americans receive a diabetes diagnoses.
Among young adults, diabetes is a growing concern. Approximately 208,000 American youth under the age of 20 have been diagnosed with diabetes. Type 2 diabetes, a disease which traditionally appear during adulthood, is appearing earlier and earlier.
Prediabetes, a condition which potentially leads to diabetes, affects an even higher percentage of the population. In 2012, an estimated 86 million American adults had prediabetes—a figure that has risen by seven million since 2010.
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. In the United States, it is the seventh leading underlying cause of death.
Who is at Risk of Developing Diabetes?
Doctors still don’t understand why some people develop diabetes and others do not. When it comes to type 2 diabetes, the more common of the two, there are a number of risk factors that can increase your chances of developing the disorder. They include:
- Weight. Having more fatty tissue puts you at an increased risk of developing diabetes.
- Lack of physical activity. Leading a sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk that you will develop diabetes. Physical activity can be used to help you maintain a healthy weight, use excess glucose in the bloodstream as energy, and improve your cells’ sensitivity to the horomone.
- Family history. Having a close family member or relative with type 2 diabetes increases your risk.
- Race. Though it’s not clear why, people of certain ethnicities are more susceptible to diabetes. These include Hispanics, Native Americans, Asian Americans, and African Americans.
- Age. Your risk of developing diabetes increases the older you are.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Many people may be unsure if they have managed to get diabetes. There are some telltale symptoms which will appear. If anyone feels they may have Diabetes, they should see their doctor as soon as possible. Some of the symptoms are:
- Dry Mouth
- Frequent Urination
- Constant Thirst
- Extreme Fatigue
- Blurred Vision
- Recurring Infections
- Loss of Healing Power
Dangers and Symptoms of Ketoacidosis
One of the most dangerous issues that can occur to Diabetics is that of ketoacidosis. During this, the body is generating too many ketones, because it is unable to processes the sugars within the blood. Ketoacidosis has many symptoms. Most of those are similar to those of diabetes, but can also include confusion, shortness of breath, and oddly fruity smelling breath.
Best Food to Eat for Diabetics
When it comes to managing diabetes, diet is the number one thing that people need to manage. Diet keeps a person’s blood sugar in check. Unsurprisingly this means that items which have high levels of processed sugars or of carbohydrates are a no go. Many of the best foods to eat on a diabetic diet include:
- Leafy Greens - Leafy greens are fantastic for diabetics. Really, any vegetables are.
- Fruits - Berries are especially good due to a lack of excess sugar.
- Lean Proteins - Low fat proteins like chicken and fish are fantastic options for a diabetic.
Hypoglycemia
While the dangers of high blood sugar are very well known, there is also a severe danger of low blood sugar. People often won’t recognize that their blood sugar is dropping and if it gets into hypoglycemic ranges, it can result in fainting, comas or death. The good news is most people may feel severe fatigue or dizziness when approaching those levels. A headache is often the first sign.